|
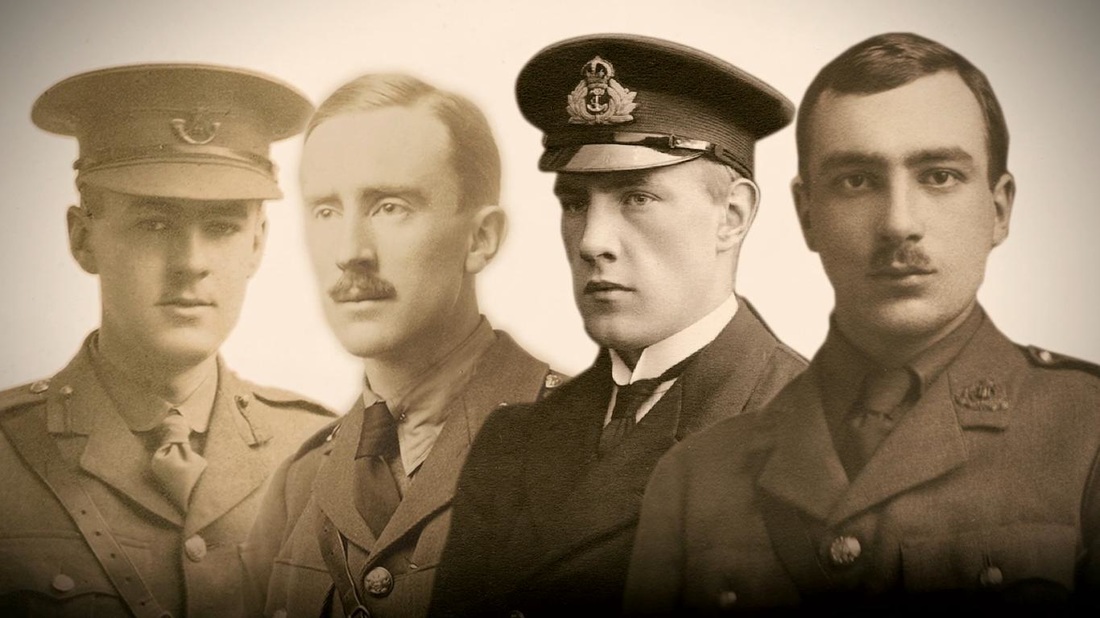
Before Tolkien was a member of the Inklings, he was a member of the TCBS. TCBS stood for Tea Club and Barrovian Society, so named because the members had surreptitious tea parties in the school library and also drank tea together at the Barrows Store. The core members of the club were four young men who had attended King Edward's School in Birmingham together, Robert Gilson, the son of the school's headmaster, Christopher Wiseman, J. R. R. Tolkien, and G.B Smith. The young men all wrote poetry, painted, and drew. They were intellectually ambitious. As a club, they hoped to spur each other on to great accomplishments. However, their youthful ambitions were tragically upended by World War 1. In the summer of 1916, exactly one hundred years ago, all four of them had shipped out to France. They spent their days marching through mud, dodging bullets and shrapnel, and crawling through trenches filled with vermin and lice. Robert Gilson was the first to die at the Somme on July first, 1916. After receiving the news, Tolkien wrote in a letter to the remaining members of the club, dated August 12, 1916 :
"So far my chief impression is that something has gone crack. I feel just the same to both of you--nearer if anything and very much in need of you--I am hungry and lonely of course--but I don't feel a member of a little complete body now. I honestly feel that the TCBS has ended . . . . Still I feel a mere individual at present--with intense feelings more than ideas of powerlessness"(Letters 10). G.B. Smith was wounded by a shell on November 29 and died of his wounds on December 3. Throughout the fall of 1916 Tolkien fought in the trenches, seeing notable action at the battle of Thiepval. He served as a signalman for the Lancashire Fusiliers sending out signals of troop movements, calls for more grenades, etc. On October 25 he visited the medical officer, complaining of a fever. He had contacted trench fever, which was caused by bites from the lice. He was sent home. Since the fever allowed him to escape from the front, it almost certainly saved his life. Already an orphan, Tolkien lost two of his closest companions that summer. The club they had created with so much youthful energy and hope, was no more. Tolkien only saw Christopher Wiseman a few times over the course of the rest of his life. Perhaps it was too sorrowful for the two of them to meet without the others. If there is something elegaic about the male friendships in The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings, that sadness is the result of the summer and fall of 1916. Tolkien's old school, King Edward's has a gallery of photos on the great war as well as a movie about Tolkien's experiences at the front made by students at the school. There is also a film about Robert Gilson. I also recommend Joseph Leconte's excellent article published this June in the New York Times about how Tolkien found Mordor in 1916 during the deadly summer of the Somme.
5 Comments
A friend of mind posted this wonderful article about Hobbit food on face-book: http://oakden.co.uk/tea-in-the-hobbit/ The amazingly gifted illustrator of John Ronald's Dragons, Eliza Wheeler, has a Hobbit party every year that she makes Hobbit food for. Perhaps this true love for all things Hobbit explains why she seems to have read my mind in composing the pictures for the book.
My favorite thing in this article is the explanation of the distinction between high and low tea. I will definitely use this article next time I take students to Oxford and will perhaps give extra points for participation in both a high and a low tea. I'm sorry that the recipes are all in UK measurements. They look quite old fashioned and complicated, just the sort of thing to make a huge mess in the kitchen, which i secretly like doing. I have not yet tried any of them out, but when I do I will write a post about it and include pictures of my creations.I may try some of them out on my next group of Oxford students. I stole the photo below from food.com. It is a photo of Mrs. Beeton's Seed Cake. Mine, when I make it, will be much less artful.  Exciting Tolkien news today. Two lost poems by Tolkien have been found. They were originally published in the obscure annual magazine of an Oxfordshire Catholic high school in 1936—an odd place for an Oxford Don to publish his work. However, Tolkien was not a professional poet, but an Anglo-Saxon scholar. His poetry, old fashioned and out of step with the high modernism of Eliot and Pound, would not have been picked up by the top literary journals. But clearly Tolkien valued it enough and believed in it enough that he wanted to see it published even in an obscure place. Also, the poem “Noel,” about the Virgin Mary, is deeply Catholic. What better place to share it than with a Catholic religious community dedicated to Mary. I like “Noel” very much. The first line: “Grim was the world and grey last night” gives the poem an alliterative Anglo-saxon flare. The description of the wintery world of the first two stanzas has much of The Wanderer and the Sea-farer in it. If the poem looks backward with its wistful romantic style to a Catholic medieval world, it also looks forward to the eucatastrophe. Tolkien was not just a man with his head turned to the past. He was always interested in uniting past and present and thereby redeeming the present. I have printed "Noel" below and here are the Guardian article and the BBC article about the poems’ discovery. NOEL Grim was the world and grey last night: The moon and stars were fled, The hall was dark without song or light, The fires were fallen dead. The wind in the trees was like to the sea, And over the mountains' teeth It whistled bitter-cold and free, As a sword leapt from its sheath. The lord of snows upreared his head; His mantle long and pale Upon the bitter blast was spread And hung o'er hill and dale. The world was blind, the boughs were bent, All ways and paths were wild: Then the veil of cloud apart was rent, And here was born a Child. The ancient dome of heaven sheer Was pricked with distant light; A star came shining white and clear Alone above the night. In the dale of dark in that hour of birth One voice on a sudden sang: Then all the bells in Heaven and Earth Together at midnight rang. Mary sang in this world below: They heard her song arise O'er mist and over mountain snow To the walls of Paradise, And the tongue of many bells was stirred in Heaven's towers to ring When the voice of mortal maid was heard, That was mother of Heaven's King. Glad is the world and fair this night With stars about its head, And the hall is filled with laughter and light, And fires are burning red. The bells of Paradise now ring With bells of Christendom, And Gloria, Gloria we will sing That God on earth is come.  It just arrived in the mail. My own copy of The Art of the Lord of the Rings by Wayne G. Hammond and Christina Scull. Their earlier book, J. R. R. Tolkien: Artist and Illustrator, was invaluable to me as I was doing my research for John Ronald’s Dragons. The book itself is beautiful: square shaped to match the square pieces of graph paper on which Tolkien sketched many of his preliminary maps. And this book is full of maps, from rudimentary squiggles on the back of discarded index cards to elaborate three color topographical masterpieces. It is also full of script. For those of you contemplating a tattoo with the ring inscription, you can choose from a whole variety of drafts photographed in this book. As a Tolkien lover, I am interested in maps and script and what they have to do with each other. And as a children’s writer I am interested in how learning to read maps is an exercise in literacy. In Maphead Ken Jennings points out that “a good map isn’t just a useful representation of a place; it’s also a beautiful system in and of itself” (7). As someone who studied linguistic systems, Tolkien would naturally be drawn to mapping. When the narrator of The Hobbit says of Bilbo, “ He loved maps, and in his hall there hung a large one of the Country Round with all his favourite walks marked on it in red ink,” we can intuit that Tolkien was also speaking of himself. Cartophilia was yet another way in which Tolkien was a hobbit. Maps are at once concrete and abstract. They represent an idea of place and space, but the representation is in symbols that we must learn to interpret: triangles for mountains, squiggly lines for rivers, etc. etc.. Ken Jennings notes the attraction he felt for maps as a child and suggests “that many people’s hunger for maps (mappetite?) peaks in childhood.” A map at the beginning of a children’s book is a promise. It promises adventure, travel, discovery, the unknown. As Nicholas Tam points out in his excellent blog, they enhance the reader's immersive experience of reading. 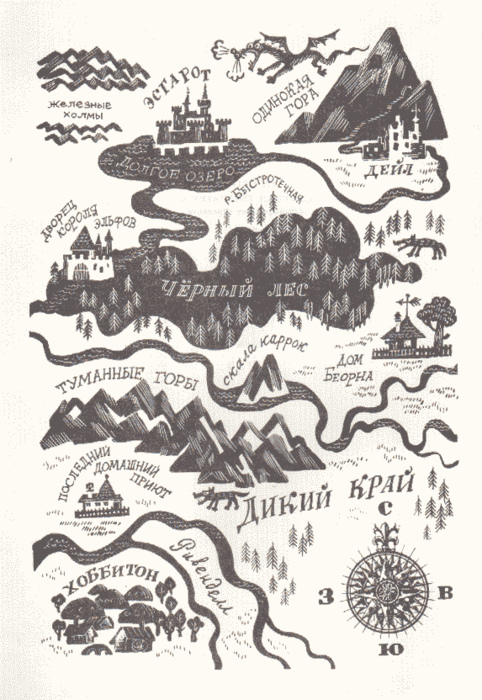 A great deal has been written by academics about maps as cultural artifacts. And several bloggers and critics have noted the charming Russian version of Thror’s map in the Russian translation of The Hobbit as proof of the cultural specificity of maps. Tolkien hated it when translators of his works attempted to translate place names, and I suspect that he might have reacted to the slavicisation of his map at the beginning of The Hobbit as he reacted to the Dutch translation of place names in his works. In a letter to his publisher, he complained: “The toponymy of The Shire . . . is a ‘parody’ of that of rural England, in much the same sense as are its inhabitants: they go together and are meant to. . . . I would not wish, in a book starting from an imaginary mirror of Holland, to meet Hedge, Duke’sbush, Eaglehome, or Applethorn even if these were ‘translations’ of ‘sGravenHage, Hertogenbosch, Arnhem, or Apeldoorn! These translations are not English, they are just homeless.” Many people have written more eloquently about Tolkien’s maps than I. Here is a wonderful blog about fantasy maps with a detailed discussion of Thror's map. And here is a review of The Art of the Lord of the Rings from Wired Magazine.  I am always fascinated by the physical ways that people write, by the technologies they choose or don't choose. There is a Royal typewriter at the Kilns, but C. S. Lewis never used it. In fact, he never learned to type at all. He wrote long hand in school exercise books and used an ink-pen that he had to dip in an inkwell--very messy and impractical. Apparently Mr.s Moore hated the inkwell, which he sometimes knocked over and spilled. But stopping to dip the pen in the well was an important part of his writing rhythm. It forced him to pause. In those pauses, he gathered his thoughts, he read the words out loud to himself (and he could hear the words without the interference of tip tapping) and he did recursive editing in his head. Lewis wrote quickly and usually did not take things through a second draft. The ink pen was the only thing that slowed him down. In this way he was the opposite of Tolkien, who composed very slowly, wrote multiple drafts and typed and retyped them himself often to save money. Overwhelmed with the expenses of having a family, he couldn't afford to pay a typist. Of course, Jack's typist was very conveniently his brother Warnie. As an army Officer in Charge of Supplies Warnie would have had to spend many hours in front of a typewriter, filling out forms. He apparently typed very fast although he only used two fingers. And he believed wholeheartedly in his brother and his genius. Typing Jack's papers and correspondence gave him a purpose and was much more fulfilling than typing forms for the army. In addition to never learning to type, Jack never learned how to drive. The scenes of him diving in Shadowlands are pure Hollywood. He loved to walk. He often walked all the way home to Headington from Oxford. He famously became convinced of the truth of Christianity while walking with Tolkien and Hugo Dyson. He took long walking tours with his brother and with other Inklings. On these tours the men would discuss philosophy, religion, and literary criticism. Somehow the movement of their legs, the rhythm of their steps would facilitate the movement of their thoughts. Thought and language are inseparable and rhythm is important to both. The Royal typewriter captures beautifully the relationship between the two brothers. It captures their different personalities; Warnie's more technological bent, his love of machines, boats, train and Jack's literary leanings, his absorption in pre-modern worlds and fantasy. It illustrates their dependence on one another. Warnie needed Jack to keep him away from alcohol, loneliness, depression. Jack needed Warnie to ground him, to remind him of his childhood and to help him type his manuscripts and organize his immense correspondence. NOTES FOR WRITERS AND TEACHERS OF WRITING
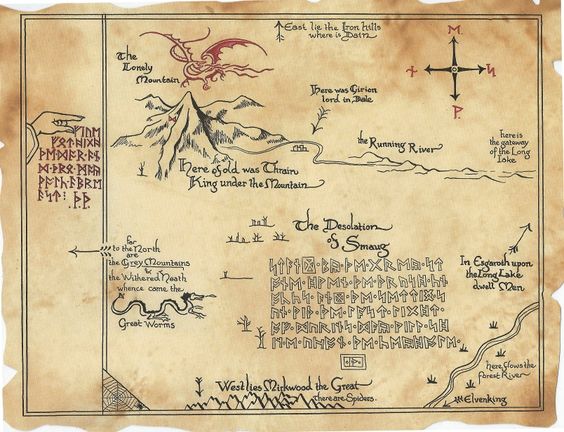
First of all, artifacts like the Royal typewriter are great sources of inspiration, great triggers for one's own writing. The Royal typewriter gave me the idea to write a book about C.S. Lewis using the angle of his friendship with his brother. Second of all, it is always good to be aware of the technologies that help us or hurt us while we are writing. What did we use when we first learned to write? What is habitual for us? Does our writing come out differently if we write a draft long hand before transitioning to the typewriter? And when we choose a technology, how much do sound, rhythm and timing matter? Computers give us the ability to compose at lighting speed, but is that always good? Do we loose the sound or sense of what we are writing if we go too fast? http://www.theguardian.com/books/2015/oct/23/jrr-tolkien-middle-earth-annotated-map-blackwells-lord-of-the-rings I was thrilled and intrigued to read about this new discovery of Tolkien “ephemera” as Blackwells calls it. The map reveals many of the reasons I love Tolkien. First of all, it shows how much his imagination was visual as well as textual and linguistic. He was a happy man with a sketch pad and a set of ink pens; his artwork helped feed his writing and vice versa. Consider the careful details that went into just the imaginary postage stamps on his Father Christmas letters. Just the lettering itself on the stamps is beautiful. Tolkien understood that text could be art and art could be text.
The discovery also reveals his love of maps, which Bilbo Baggins shared with him. “He loved maps, and in his hall there hung a large one of the country round with all his favorite walks marked on it in red ink.” Maps were integral to Tolkien’s fantasy worlds, to his plots, to his writing process. As writers we could all learn from him to do more mapping. And most importantly of all, the detailed annotations reveal his scholarly, curmudgeonly insistence on perfection. They reveal his desire to control how his work was printed and transmitted down to the smallest minutiae. Hooray for Tolkien! What a great find! |
Caroline McAlisterCaroline is an avid reader, children's writer, and teacher. She lives in North Carolina with her husband and dog. Check out her bio for more! Archives
February 2024
Categories
All
|




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed